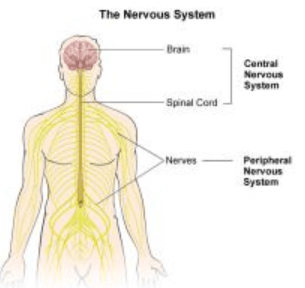
The human nervous system is divided into (1) the central nervous system (CNS) which includes the brain and the spinal cord and (2) the peripheral nervous system (PNS) which consists of nerve cells that carry information to or from the central nervous system.
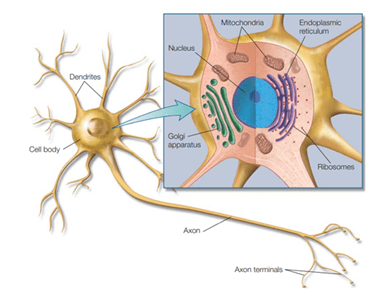
The nervous system is composed of two main classes of cells: neurons and glial cells. Neurons are cells adapted to carry information by means of electrical impulse throughout the nervous system.
Neuron Structure
The neuron structure has the main components of any cell: it has a cell membrane around the cell body. The cell body in a neuron is called the soma. The soma or cell body has the metabolic machinery that includes a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and other common intracellular organelles.
USA, New York: WW Norton Company
These intracellular structures are suspended in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a “salty” intracellular fluid that is made up of a combination of ions, predominantly, ions of potassium (K+), chloride (Cl–), and Calcium (Ca+), as well as other molecules such as proteins.
Dendrites are branching extensions of the neuron that receive inputs from other neurons. The axon is a single process that extends from the cell body. Electrical signals travel along the length of the axon to its end, the axon terminals, where the neuron transmits the signal to other neurons or other cell types.
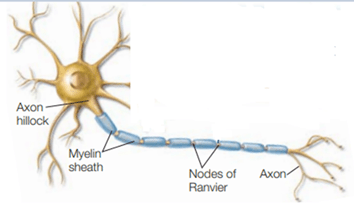
Many axons are wrapped in layers of a fatty substance called myelin. Along the length of the axons, there are evenly spaced gaps in the myelin. These gaps are the nodes of Ranvier. Myelin and the nodes of Ranvier has a role in accelerating signal transmission.
Neurons communicate with other neurons and cells at specialized structures called synapses, where chemical and electrical signals can be conveyed between neurons.
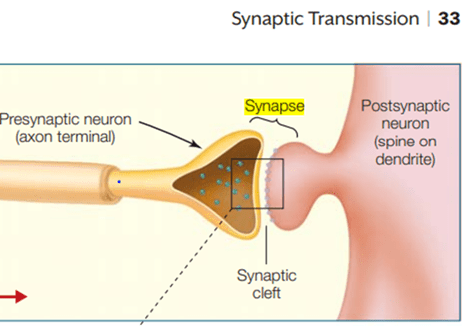
Transmission occurs at the synapse, a specialized structure where two neurons come into close contact so that chemical or electrical signals can be passed from one cell to the next.
Source: Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R. & Mangun, G. (2018). Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind. (5th ed.). USA, New York: WW Norton Company.
